by Mikayel Vardanyan
| Jun 05, 2011

1. OpenVZ (http://wiki.openvz.org)
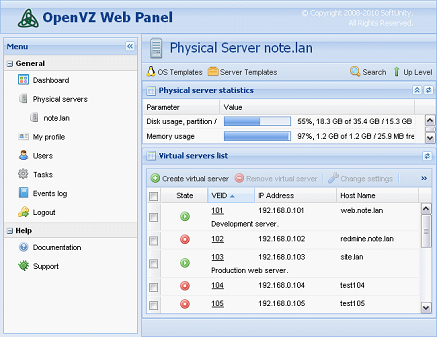
The OpenVZ kernel is a free modified Linux kernel software component of SWsoft’s Virtuozzo, which adds the following functionality: virtualization and isolation of various subsystems, resource management, and check pointing.
Pros
- Great for tasks requiring having not to run multiple OSes, but rather just multiple guests, in order to make the most of hardware or provide separation between services (for instance, separating your Web server from your file and print server) with minimal overhead.
- Supports more processor platforms than its competitors.
- Excellent documentation available.
Cons
- The application does not provide the ability to run multiple OSes.
- Does not have loadable kernel modules, and is not fully isolated. Having multiple users can slow down everyone’s VPS.
- If one machine is struggling for ram/heavily swapping, the kernel will kill off processes to free ram.
- Is only for the Linux platform.

2. Xen (www.xen.org)

Xen is a powerful open source industry standard for virtualization, which offers a powerful, efficient, and secure feature set for virtualization of x86, x86_64, IA64, ARM, and other CPU architectures.
Pros
- Can run on any platform without hardware support.
- Has more active users worldwide than its nearest competitors.
- Provides guaranteed allocation that does not take away resources from the other users on the node.
Cons
- Slightly higher overhead than OpenVZ, it’s not as well documented. If you want to know it well you will need to do some digging round the web.
- Initial configuration can be more complex than other competitive products.

3. Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) (www.linux-kvm.org)

As a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V), KVM is a virtual machine implementation that uses the operating system’s kernel for greater performance.
Pros
- Extremely scalable, while running very large guests.
- Provides real-time scheduling capabilities
Cons
- Requires hardware assistance in order to run
- Lacks the ability to provide device assignment
- Does not provide efficient memory and power management.

4. Linux-VServer (http://linux-vserver.org)
Linux-VServer technology allows the creation of many independent Virtual Private Servers (VPS) that run simultaneously on a single physical server at full speed, providing an efficient way to share hardware resources.
Pros
- Very simple to implement in comparison to similar platforms.
- Provides excellent performance as it offers a simple method to running virtual servers on one piece of physical hardware.
Cons
- VMS have to be for the same distribution as they share a kernel
- The application’s networking is not virtualized

5.VirtualBox (www.virtualbox.org/)
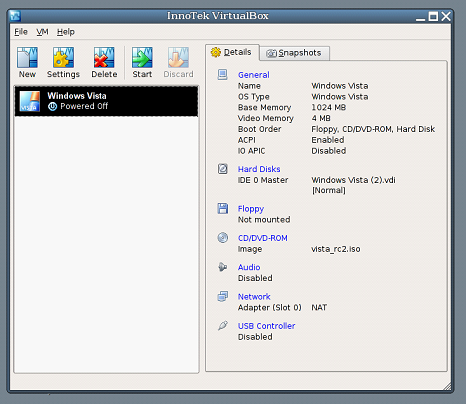
VirtualBox is an x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization product for both commercial and home use. VirtualBox is freely available as Open Source Software and runs on Windows, Linux, Macintosh and OpenSolaris hosts and supports a large number of guest operating systems.
Pros
- Very easy to install without adding device drivers and services.
- Great for home use with the capabilities found in commercial applications.
- Provides excellent memory management, in addition to delivery superior performance in both windows and Linux.
Cons
- Includes limited options for management and monitoring of the resources of virtual machines.
- Can be slow to load at times.
- Loading an operating system from a CD can be difficult at times.
Mon.itor.Us is a free server monitoring service based in the Cloud, the first in the world, that monitors both external factors, including application uptime and end-user experience, and internal server resources such as disk space usage, memory, CPU and traffic. Singup free server monitoring service now and have your monitoring ready in 5 mins.